Recently, NavInfo Co., Ltd., Urban Traffic Engineering Technology Center of Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development and China Academy of Urban Planning & Design jointly released 2019 Annual Report on Road Network Density in Major Chinese Cities (hereafter referred to as "the report"). The professional big data company Cennavi subordinate to NavInfo have provided this report with the relevant work support such as the map data and big data analysis, marking that the map data and big data have the important position and role in the field of urban planning.

Figure 1 the Cover of Annual Report on Road Network Density in Major Chinese Cities
In order to further implement the spirit of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China and the Urban Work Meeting of the Central Government, actively implement the relevant requirements in Several Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Further Strengthening the Management Work of Urban Planning and Construction (ZFa [2016] No. 6), orderly promote the construction of urban traffic infrastructures, accelerate the supplement of weakness of the traffic infrastructures, promote the implementation of the urban road layout concept "narrow road, dense network", construct the road network system of reasonable gradation and improve the passing efficiency and bearing capacity of the urban road network,
and entrusted by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-rural Development, Urban Traffic Engineering Technology Center of Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, China Academy of Urban Planning & Design joined forces with NavInfo Co., Ltd. jointly to carry out the work of monitoring and studying the road network density in major Chinese cities and completed the compilation of 2019 Annual Report on Road Network Density in Major Chinese Cities.
Based on the first version of the report in 2018, 2019 Annual Report on Road Network Density in Major Chinese Cities continued to take 36 major Chinese cities as the study objects, tracked and monitored the development condition of the road network density in these cities, including 4 municipalities directly under the central government, 27 provincial capitals and 5 cities specifically designated in the state plan. As of the end of 2018, the overall average road network density in 36 major Chinese cities had been 5.96km/km2, with the overall growth rate of 1.24% compared with the average density of 5.89km/km2 in 2018, which still had a big gap with the objective that "the average road network density shall be improved to 8km/km2 in the built-up areas in the cities" put forward in Several Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on Further Strengthening the Management Work of Urban Planning and Construction.
According to the report, among 36 major Chinese Cities, Shenzhen, Xiamen and Chengdu were still the cities where the road network density was at a higher level (the road network density reached more than 8.0km/km2), accounting for 8%. There were 19 cities where the road network density was at the intermediate level (the road network density was between 5.5km/km2 and 8.0km/km2), including Shanghai, Guangzhou and Fuzhou, accounting for 53%. There were 14 cities where the road network density was at a lower level (the road network density was lower than 5.5km/km2), accounting for 39%.
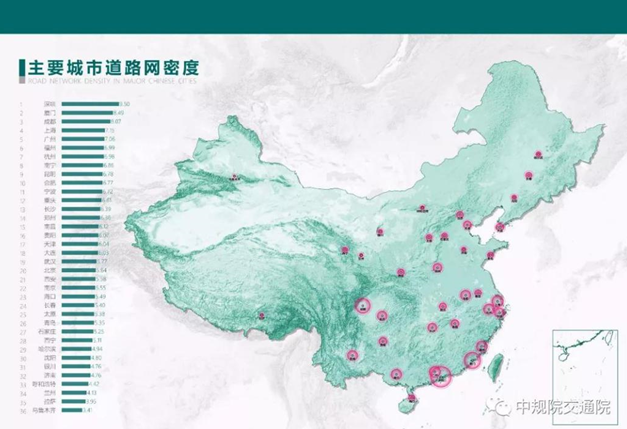
Figure 2 Overall Situation of Road Network Density in Major Cities
Based on the monitoring data of the road network density for two consecutive years from 2018 to 2019, the road network density in 36 major Chinese cities and their administrative districts presents the following rules:
1. The road network density in most cities presents the growth trend, and the overall ranking of cities is relatively stable
Compared with the road network density in 2018, among 36 major Chinese cities, the road network density index in 25 cities realized a certain degree of growth, while the road network density index in 11 cities basically remained unchanged. The ranking of 7 cities including Fuzhou and Nanning was on the rise; that of 6 cities including Hangzhou and Kunming dropped, and that of 20 cities including Shenzhen and Xiamen remained unchanged.
In 2019, the road network density index in 5 cities including Shenzhen, Xiamen, Chengdu, Shanghai and Guangzhou still remained Top 5, with the same ranking as in 2018, and Shenzhen, Xiamen and Chengdu reached the target requirement of 8km/km2 put forward by the state. 4 cities where the overall road network density remains at a lower level are Hohhot, Lanzhou, Lhasa and Urumqi respectively, with the same ranking as in 2018, and their density is lower than 4.5km/km2. Among four first-tier cities, ranking of the road network density level is respectively Shenzhen > Shanghai > Guangzhou > Beijing.
2. The road network density in cities remains a stable growth rate, while Lhasa, Nanning, Hohhot and Taiyuan show a rapid growth
From the annual growth conditions of the road network density in major Chinese cities, in 2019, there are 4 cities where the growth rate of road network density is higher than 4%, among which Lhasa has the highest annual growth rate of road network density (4.50%), followed by Nanning (4.41%), Hohhot (4.25%) and Taiyuan (4.06%).
With Nanning City as an example, the overall road network density in Nanning is 6.86km/km2, with the density growth rate of 4.41%, wherein Yongning District, Xixiangtang District and Xingning District show a relatively rapid growth, entering into Top 20 in the growth ranking of density in the administrative districts. In 2019, the new road mileage of about 78km has been increased in the central urban area of Nanning. It can be seen from the incremental analysis of the road network that the road construction such as Qingxiang Expressway in Nanning City, Longgang Avenue Area in Yongning District and Pingle Avenue Area in Liangqing District has a great influence on the promotion of overall road network density in the cities.
3. The growth rate of the road network density in the peripheral new urban area is obviously higher than that in the central old urban area
Based on analyzing the overall road network density in major Chinese cities, the report further studied the road network density in the major administrative districts in the cities. In 2019, the average value of the road network density in all the administrative districts involved is 6.30km/km2, with an overall average growth rate of 0.96% compared with the average value of 6.24km/km2 in 2018.
The number of the administrative districts where the road network density has reached the standard among 214 administrative districts is still 34, the same as that in 2018, only accounting for 16%. Among them, there are 7 administrative districts whose road network density has exceeded 10km/km2, accounting for 3%, and there is only Huangpu District of Shanghai whose road network density has exceeded 12km/km2 (14.31km/km2). It's worth noting that the median value of density in 214 major administrative districts (counties) was 5.88km/km2 in 2018, while the median value of the road network density index in 2019 has been promoted to 6.14km/km2.
From the growth situation of the road network density in the administrative districts of major Chinese cities, among 214 major administrative districts, there are 3 administrative districts whose growth range of the road network density has exceeded 10%, which are Wangcheng District of Changsha, Hunnan District of Shenyang and Xinghualing District of Taiyuan. There are totally 19 administrative districts with the growth range of 5%-10%, mainly including Wanbailin District of Taiyuan, Yongning District of Nanning, Shapingba District of Chongqing and Xixiangtang District of Nanning, accounting for about 9% of all the administrative districts in the statistics.
The road network density in the peripheral administrative districts of the cities shows a relatively rapid growth. From the perspective of the major administrative districts ranking Top 20 concerning the growth rate of density index, the characteristic the peripheral administrative districts of the cities have dominated has been presented, such as the growth rate of Wangcheng District of Changsha up to 16.1%, that of Hunnan District of Shenyang up to 11.1% and that of Xinghualing District of Taiyuan up to 10.3%. Other administrative districts with higher growth rate, such as Yongning District of Nanning, Yuhong District of Shenyang, Xincheng District of Hohhot, Beibei District of Chongqing and Mawei District of Fuzhou are the peripheral administrative districts of cities.
As the peripheral new urban area of the cities has been continuously developed and constructed and a lot of road infrastructures have been completed and put into use, the road network density in the peripheral administrative districts has been improved.
Comparatively, in the central old urban area of the cities represented by Jing'an District of Shanghai, Yuzhong District of Chongqing and Shangcheng District of Hangzhou, the road network density index basically remains stable for such reasons as finalization of road network in the cities, small increment of new road facilities and reconstruction and upgrading of few roads.

Figure 3 Summary of the Road Network Density in the Administrative Districts of Cities
Annual Report on Road Network Density in Major Chinese Cities utilized the advanced informatization means to set up the monitoring platform for the road network density in the cities, realized the dynamic monitoring of the road network in the cities and overcame the problems in the traditional urban work such as the inconsistent statistics standards for the road network density and poor timeliness of data updating, providing effective support for reasonably controlling the road network density in the cities and promoting the implementation of urban traffic planning. The monitoring platform for the road network density will continuously concern and study the road network changes in the major Chinese cities and regularly provide the monitoring report.


